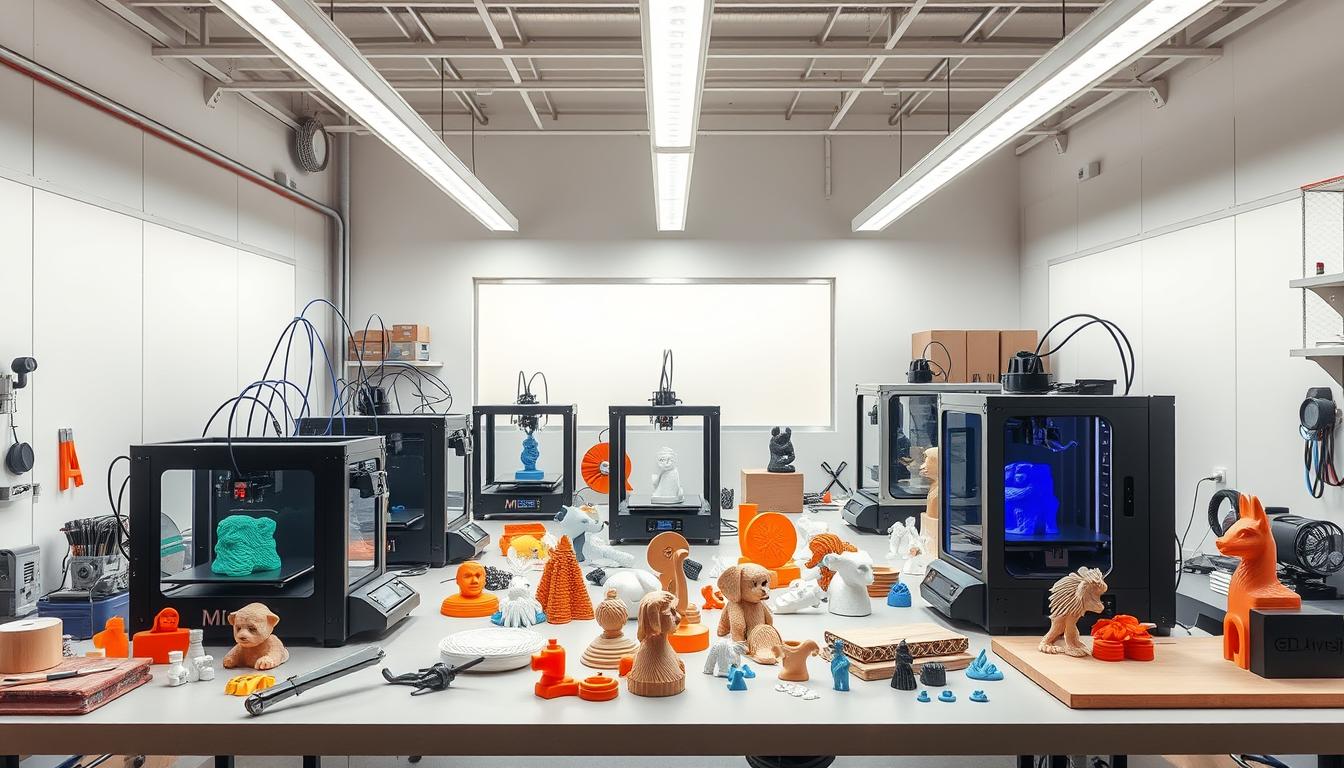
Imagine walking into a design studio where ideas come to life in hours. A small fashion startup experienced this, using 3D printing to make detailed jewelry. They didn’t wait weeks for samples like before. Instead, they printed prototypes overnight, saving time and getting instant feedback.
This led to quicker product launches that wowed customers. As more businesses use industrial 3D printing, production and prototyping are changing. This guide will show how 3D printing is a game-changer for today’s fast market.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing revolutionizes prototyping and manufacturing processes.
- Additive manufacturing services enhance design flexibility and customization.
- Industrial 3D printing minimizes lead times and accelerates product development.
- The technology enables cost-effective solutions with reduced waste.
- Real-time collaboration improves iteration and innovation.
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
3D printing changes how we design and make things. It uses digital files to build objects layer by layer. This method is fast and precise, helping designers create and test ideas quickly.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a way to make three-dimensional objects from digital models. It works by adding material layer by layer until the object is complete. This is different from old methods that take more time and waste material.
Types of 3D Printing Techniques
There are many 3D printing methods, each with its own way of working:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) – This method uses a heated nozzle to layer thermoplastic filament, creating solid objects.
- Stereolithography (SLA) – SLA uses UV light to harden liquid resin, making it great for detailed work.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) – SLS fuses powdered material with a laser, creating strong and complex parts.
Materials Used in 3D Printing
The materials used in 3D printing depend on what you need:
| Material Type | Common Applications | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | Prototypes, consumer products | Flexible, easy to mold |
| Metals | Aerospace, automotive, medical | High strength, durability |
| Composites | Engineering, custom designs | Lightweight, enhanced stability |

Advantages of 3D Printing in Prototyping
3D printing has changed the way we make prototypes. It makes product development faster and more efficient. Companies using 3D printing see big changes in how they work on projects.
Speed and Flexibility
Designers can make prototypes much quicker with 3D printing. This quickness lets them change designs easily. They can get feedback fast and make changes without waiting long.
Cost-Effectiveness
3D printing saves money. It uses less material, which cuts down on costs. Unlike old methods, 3D printing doesn’t need expensive tools or setup. This makes it easier for teams to work within tight budgets.
Enhancing Collaboration and Iteration
3D printing helps teams work better together. They can make and share models fast. This makes it easier to talk about design changes and keep improving without delays.

| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed | Rapid prototyping allows for quick development cycles. |
| Flexibility | Easy modifications of designs in real-time. |
| Cost Reduction | Less material waste and no need for expensive tooling. |
| Collaboration | Encourages team feedback and iterations on prototypes. |
3D Printing in Manufacturing Applications
3D printing is changing how we make products. Companies like Boeing and General Electric are using it to make parts for their products. This shows how 3D printing can make production faster and reduce waste.
Real-World Examples of 3D Printing
3D printing is changing many industries. Boeing uses it to make parts for planes, making them lighter and more fuel-efficient. General Electric uses it for turbine parts, making production faster and keeping quality high. These examples show how 3D printing can improve products.
Challenges and Considerations in Manufacturing
But, there are challenges with 3D printing. Companies must follow rules and deal with material limits. They also need to make sure 3D printing fits with their current ways of making things.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Industry
The future of 3D printing looks bright. New technologies like multi-material printing are coming. These will help solve current problems and make production more efficient. As we want to make things more sustainably, 3D printing will play a big role in the future of making things.